Skin Cancer
Malignancies of the skin are the most commonly diagnosed cancer type worldwide.(1) The foremost cause of skin cancer remains UV radiationfrom sunlight.
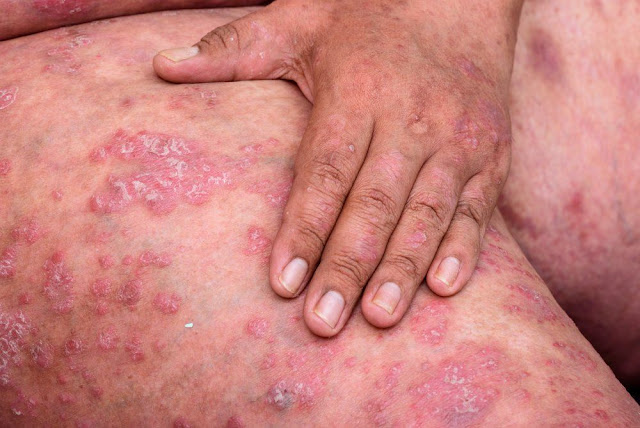
Superficial spreading: The most frequently observed melanoma. This form may develop in any region of the skin. Lesions are usually raised around the edges and a brown color with hints of pink, white, gray and blue.
Nodular type lesions: Also arise on all regions of the body and are typically black or brown in color.
Acral lentiginous lesions: Characterized by flat, brown or black tumors that often develop on the hands and feet.
Lentigo maligna melanoma: Develop on an individual's face. Distinguished by its irregular border and tan to brown color.
Skin Cancer: Symptoms and Detection
The American Academy of Dermatology and the American Cancer Society recommend that individuals perform monthly self-examinations.(1) It is important to keep the ABCDE's (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolution) of melanoma in mind.
Asymmetry: melanomas tend to be asymmetrical while benign lesions are more rounded and symmetric.
Borders: Benign lesions are usually regular and flush with the skin while melanomas may have irregular and/or raised borders.
Color: Melanomas may be tan, black or brown and often include regions of red, white and blue.
Diameter: In general, melanomas are larger than 6 mm in diameter.
Evolution: Changes in physical appearance of melanocytic growths are often observed over time and skin marking should be monitored for changes. Because the changes may be gradual, it is a good idea to photograph any suspicious marks, including a ruler or coin for size comparison. This allows for direct comparison of images taken at different times.
Although the ABCDE guidelines assist with a valuable screening tool, it is important to see a physician regularly and especially if one finds a suspicious or irregular skin marking/growth or witnesses a change in an existing skin marking/growth.
However, this disease, classically seen in older adults, is becoming increasingly common in younger populations due to tanning beds and exposure to other cancer causing elements.

Skin cancer may be classified as either non-melanoma skin cancer (cancer types include squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma) or melanoma.
The most common type of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma. However, melanoma which accounts for only 4% of skin cancer is responsible for 80% of skin cancer deaths.
(1)The incidence of skin cancer is very high. It is the most diagnosed of all cancers. However, there aren't many exact numbers because the cases of basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers aren't required to be reported to cancer registries, partly because of their low lethality and very high curability rate.
At the least, it is known that over 2 million people were treated for these cancers in 2006. Melanomas, on the other hand, have a very high mortality rate that has been increasing over the several decades, especially among younger women and the elderly, so there is much more data on this. In 2010, it is estimated that there will be 68,130 cases of melanoma and 5,880 cases of other non-epithelial skin cancers, with 8,700 deaths for melanoma and 3,090 deaths for non-epithelial.
(2)Young men DO get cancer. View the clip and then watch an interview with Philip Groom, a skin cancer survivor diagnosed when he was 16 years old.
Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer may be divided into two types: non-melanoma and melanoma.
Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
There are two major sub-types of non-melanoma skin cancer:
Basal Cell Carcinoma- The most commonly diagnosed skin cancer.
Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer may be divided into two types: non-melanoma and melanoma.
Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
There are two major sub-types of non-melanoma skin cancer:
Basal Cell Carcinoma- The most commonly diagnosed skin cancer.
Tumors often develop on regions of the body that receive regular sun exposure such as the face and hands. Due to its slow growth rate, basal cell carcinoma rarely spreads and is usually treatable.
(1) A common form of basal cell carcinoma is nodular basal cell.
Lesions appear as a pearly nodules in various colors including brown, black and blue.
(2)Squamous Cell Carcinoma- Appears on body parts that experience increased levels of sun exposure such as the face, lips and back.
(1)This cancer is more likely to spread than basal cell carcinoma. The cancerous lesions have numerous forms. They may be rough, scaly, lumpy or flat. Blood vessels may appear at the edge of a lesion causing it to bleed easily.
(2)Melanoma is a cancerous growth of melanocytes and most frequently develops in the skin.
(3) Melanoma may also develop in other parts of the body that contain melanocytes including the meninges, the digestive tract, the eyes and lymph nodes. The following descriptions are limited to melanoma of the skin.
There are several types of melanoma that can be categorized based on their appearance, either with the naked eye or microscopically:
There are several types of melanoma that can be categorized based on their appearance, either with the naked eye or microscopically:
Superficial spreading: The most frequently observed melanoma. This form may develop in any region of the skin. Lesions are usually raised around the edges and a brown color with hints of pink, white, gray and blue.
Nodular type lesions: Also arise on all regions of the body and are typically black or brown in color.
Acral lentiginous lesions: Characterized by flat, brown or black tumors that often develop on the hands and feet.
Lentigo maligna melanoma: Develop on an individual's face. Distinguished by its irregular border and tan to brown color.
Skin Cancer: Symptoms and Detection
The American Academy of Dermatology and the American Cancer Society recommend that individuals perform monthly self-examinations.(1) It is important to keep the ABCDE's (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolution) of melanoma in mind.
Asymmetry: melanomas tend to be asymmetrical while benign lesions are more rounded and symmetric.
Borders: Benign lesions are usually regular and flush with the skin while melanomas may have irregular and/or raised borders.
Color: Melanomas may be tan, black or brown and often include regions of red, white and blue.
Diameter: In general, melanomas are larger than 6 mm in diameter.
Evolution: Changes in physical appearance of melanocytic growths are often observed over time and skin marking should be monitored for changes. Because the changes may be gradual, it is a good idea to photograph any suspicious marks, including a ruler or coin for size comparison. This allows for direct comparison of images taken at different times.
Although the ABCDE guidelines assist with a valuable screening tool, it is important to see a physician regularly and especially if one finds a suspicious or irregular skin marking/growth or witnesses a change in an existing skin marking/growth.



Comments
Post a Comment