Few things to know about Eczema
Eczema is not a specific illness but is a term that describes a group of inflammatory skin conditions that cause rash-like symptoms such as red itchy spots on the skin.
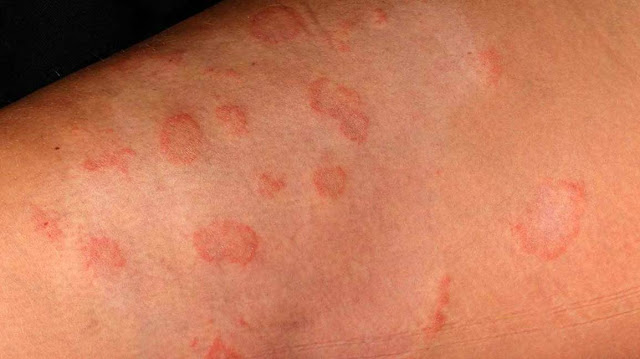
It is also known as dermatitis (skin inflammation), atopic eczema (“atopic” means the genetic predisposition to allergic hypersensitivity), or simply atopic dermatitis.
The term "atopic dermatitis" may be used interchangeably with "atopic dermatitis", even though clinically atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. Often.
Eczema is the most severe and chronic (long-lasting) form of eczema. It is characterized by the skin becoming inflamed and the clear liquid tearing and releasing when scratched (an effect known as bleeding). According to the National Institute of Arthritis, Musculoskeletal, and Skin Diseases, people with atopic dermatitis often relapse when their symptoms worsen and relieve when their symptoms improve or resolve.
The term "atopic dermatitis" may be used interchangeably with "atopic dermatitis", even though clinically atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. Often.
Eczema is the most severe and chronic (long-lasting) form of eczema. It is characterized by the skin becoming inflamed and the clear liquid tearing and releasing when scratched (an effect known as bleeding). According to the National Institute of Arthritis, Musculoskeletal, and Skin Diseases, people with atopic dermatitis often relapse when their symptoms worsen and relieve when their symptoms improve or resolve.
Causes
Damage to the skin barrier that prevents oil storage while promoting water loss causes eczema. Scientists don't know why this happens, but genetics may play a role. Family or personal history of asthma or hay fever is a risk factor.Types Includes:
- Contact Eczema (Contact Dermatitis): This type of eczema is a localized skin reaction to a substance in the environment that causes the skin to become red and itchy.
- Hand Eczema: If you have dry, thick, scaly patches on the hands that may crack and bleed (like contact eczema), you may have hand eczema. Various irritants and allergens may be responsible for a hand eczema flare.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Small, itchy blisters on the soles of the feet and edges of the fingers, toes, and palms may be signs of dyshidrotic eczema. Stress and allergies are two possible triggers for this form of eczema.
- Nummular Eczema: Compared to other types of eczema, nummular eczema appears differently: as itchy, coin-shaped spots on the skin.
- Stasis Dermatitis: This occurs when fluid leaks out of the veins and into the skin due to blood flow issues.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Seborrheic dermatitis happens when white or yellow scaly patches of skin develop in oily areas, such as the scalp (as dandruff), face, and ears, partly as a result of microorganisms that live on the skin (such as some types of yeast).
There is no cure for eczema, but avoiding known triggers and using treatment options can help relieve symptoms. First, moisturize the skin with an unscented cream or ointment. Topical corticosteroids and oral medications can help reduce irritation and prevent relapse.
Foods you should avoid if you have eczema
The possible link between eczema and diet is unknown. However, some people with atopic dermatitis, especially children, may have food allergies at the same time. There is no evidence that a diet alone can cure eczema, but avoiding certain anti-inflammatory foods can alleviate the symptoms of some individuals.
What home remedy can one use for eczema?
The possible link between eczema and diet is unknown. However, some people with atopic dermatitis, especially children, may have food allergies at the same time. There is no evidence that a diet alone can cure eczema, but avoiding certain anti-inflammatory foods can alleviate the symptoms of some individuals.
To treat eczema at home, moisturize the skin with creams and ointments. Complementary therapies include coconut oil and sunflower oil, a topical ointment containing heart sperm or heart seeds, and a B12 compound called Pink Magic. Stress relief approaches such as meditation and massage can also help reduce relapses.



Comments
Post a Comment